Space
-
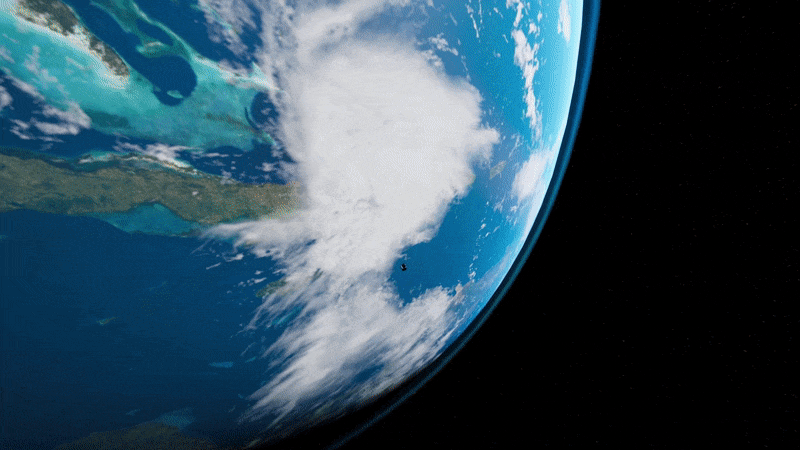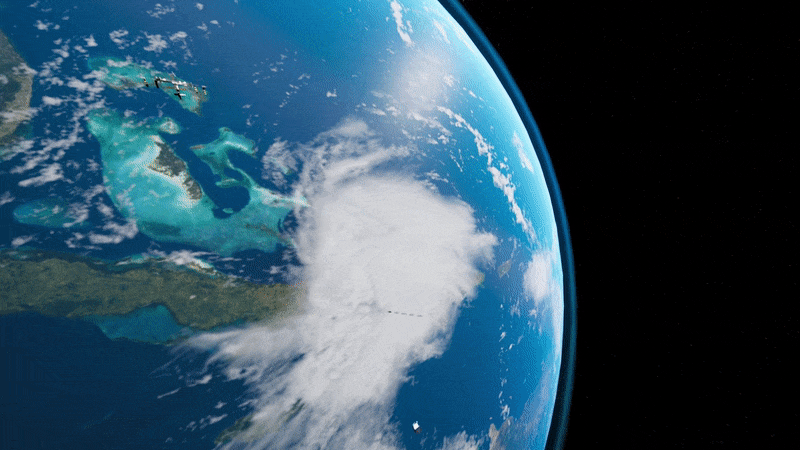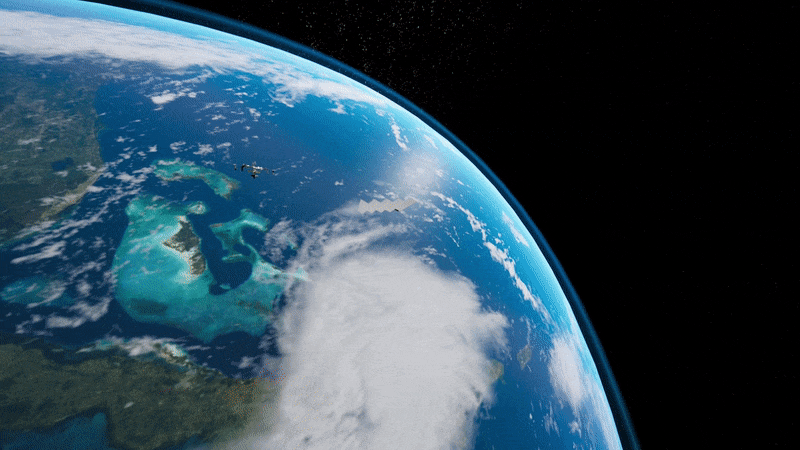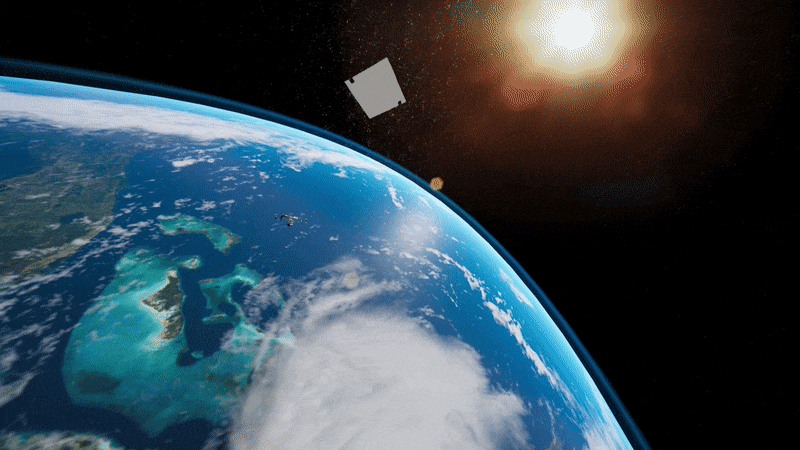
Light sail deployment simulation
Simulation of on-orbit free-flying light sail deployment from the Cornell Alpha CubeSat, developed and choreographed in Unreal Engine 4. Alpha will carry the world’s first retroreflective, solo-flying light sail—and become the trailblazer for future missions to our nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri.
-
Detecting Cloud Cover from Space Using Infrared Sensors (Miami Young Data Scientists)
We had the opportunity to run our code on-orbit aboard Spire Global’s Lemur 2 NanoSatellite as part of a winning experimental machine learning entry in the 2015 Association of Space Explorers (ASE) Astrosat Challenge.
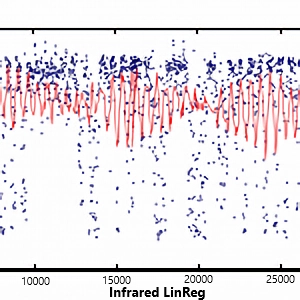
Data collection was constrained to 15 kilobytes, approximately 1500 observations, from an equatorial orbit. Used a support vector machine approach on infrared emissivity data to predict cloud cover, validated with live weather apis.
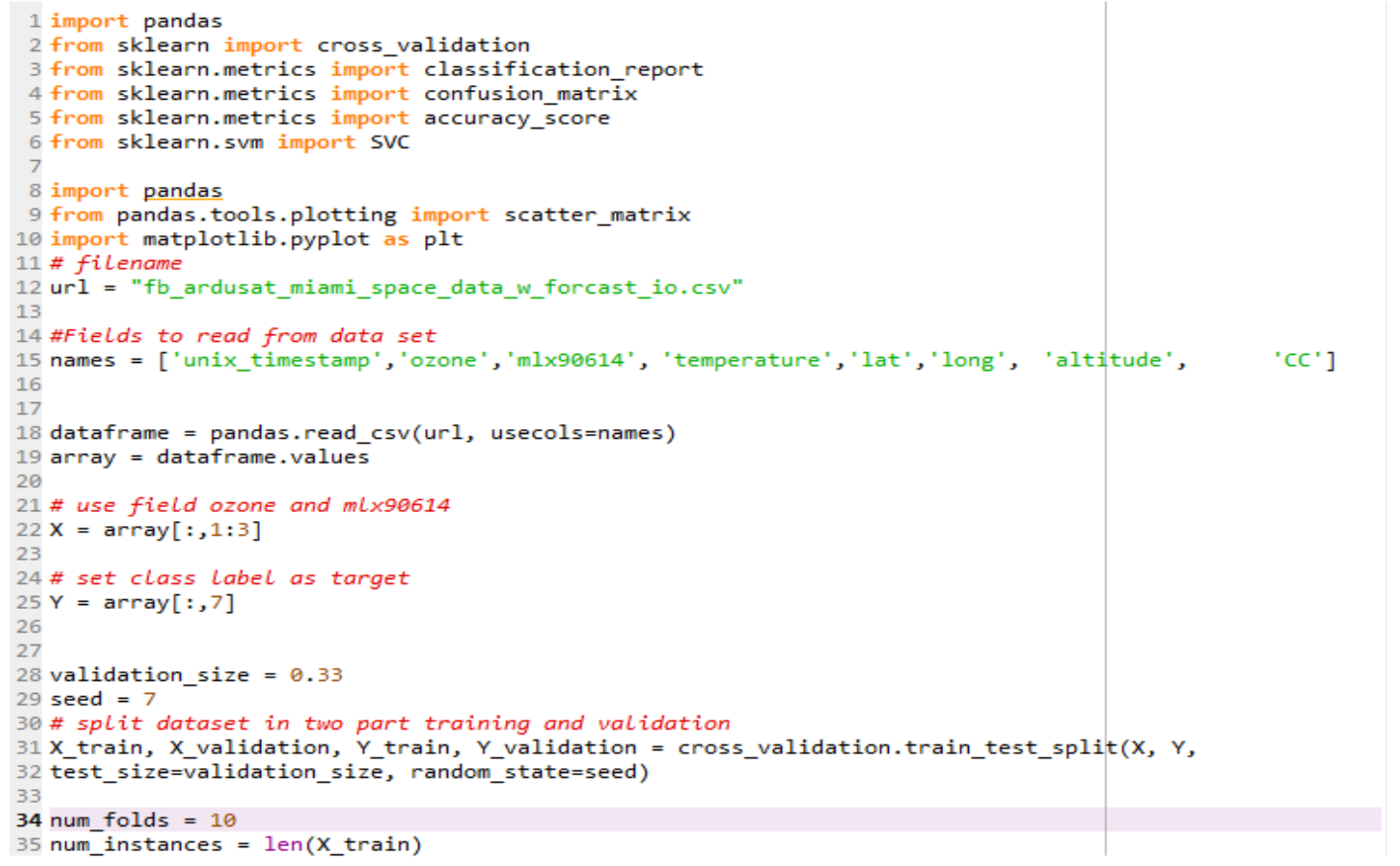
Achieved approximately 75% accuracy in the binary classification problem (is it a cloud or not?).
My teammate and I delivered our findings to the local Miami tech community with the Countdown Institute and taught introductory space and data science to local students.